If you notice yellow leaves on your roses in early spring, it could be a sign of certain problems. Addressing these issues in a timely manner will keep your roses healthy and thriving for the spring bloom.
Common Causes and Treatments for Yellow Leaves on Roses in Early Spring
Due to climate differences in different regions, roses will grow in different states. Below are the common problems and solutions for different regions, you can match them to your geographic location. (In the cold regions of the north, roses are still in the dormant stage, so they will not be introduced.)
1. Southern (Guangdong, Fujian) regions
In the south, where winters are warm, roses do not go dormant, and usually by March, roses have begun to produce flower buds in large numbers. At this stage, metabolic yellow leaves are rare. If your roses show a lot of yellow leaves at this time, you need to pay special attention to the following possible problems:
① Fertilization

Roses are in a rapid growth phase and need more nutrients, so many gardeners will fertilize frequently or apply large amounts of fertilizer. However, once too much fertilizer is applied, especially if the concentration of fast-acting water-soluble fertilizer is too high, it is easy to cause fertilizer damage. Even if water-soluble fertilizers are applied only once a year, if the concentration is too high, it may cause the tips or edges of the leaves to dry up and yellow, or even the whole plant to wilt.
To avoid fertilizer damage, when using water-soluble fertilizers, be sure to read the instructions carefully and reduce the concentration appropriately. For weaker plants, it is recommended to dilute further than the recommended concentration to ensure safety.
② Excessive drought
Roses need adequate water support during the peak growth period, especially during the bud-bearing period. If watering is not timely, resulting in overly dry potting soil, roses may exhibit a large number of yellow leaves. You should keep sufficient fertilizer and water in spring, and adjust the amount and frequency of watering according to the weather and the plant’s growth status.
2. Frosty areas around Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Shanghai
In the frosty areas of Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Shanghai, most of the roses planted in the open air are now in the state of sprouting new buds, or the new buds have just grown two or three centimeters. If you find a lot of yellow leaves on roses at this time, you may need to focus on the following aspects:
① Inadequate pruning: a large number of weak branches sprouting weak buds
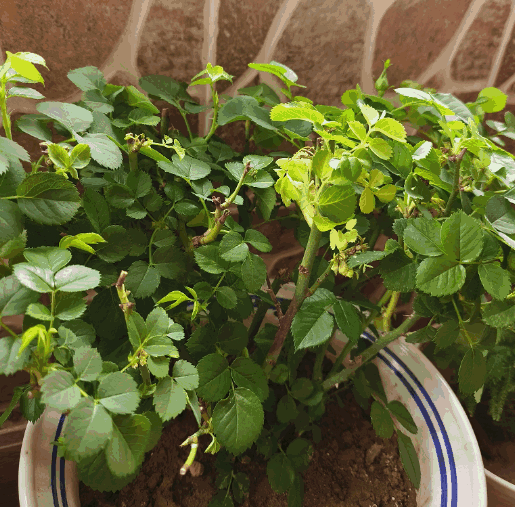
The picture below is a case of a florist inquiring about yellow leaves, which is usually caused by poor pruning. When pruning roses in winter, you should cut off small, weak branches and branches with poor bud points. In addition, when roses germinate in early spring, it is also important to observe closely and promptly prune away stunted buds or branches with low vigor, retaining only the strong branches and new buds.
If a large number of weak buds sprout and yellow leaves appear due to improper pruning, supplementary pruning can be done directly.
② Fertilizer/medicine damage causing deformed yellowing of new shoots
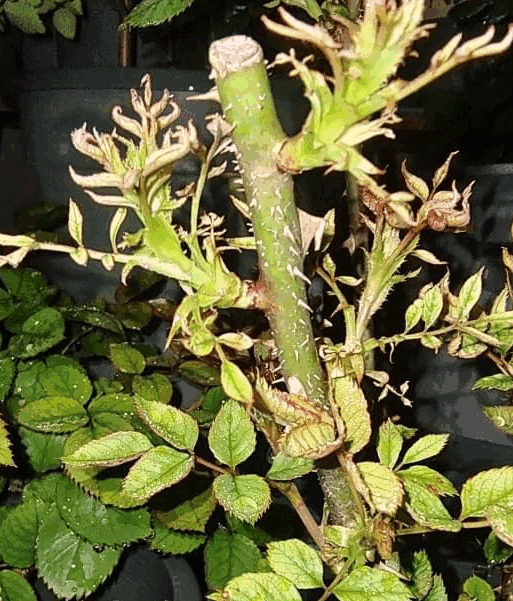
New leaves of early spring roses may appear misshapen and of an abnormal color (e.g., not green enough or unevenly red). If this occurs, the following two causes need to be considered:
a. Fertilization damage
Fertilizer damage may be caused by too high a concentration of water-soluble fertilizer applied retroactively, or by too much organic or slow-release fertilizer applied in winter or early spring, even close to the roots. If fertilizer damage is not very serious, the new leaves may gradually return to normal as the rose grows and no special treatment is needed.
However, if the symptoms of fertilizer damage are obvious, timely measures are needed. If the fertilizer damage is caused by water-soluble fertilizers, it can be relieved by pouring a lot of water on the roots; if it is caused by long-lasting fertilizers, it is necessary to dig out part of the fertilizers or even replace the soil.
b. Drug damage
Drug damage usually manifests itself in the form of dotted and scattered scarring on the leaves. Since the symptoms of drug damage and fertilizer damage are similar, the exact cause needs to be determined in conjunction with your management records. For example, if you have recently sprayed pesticides at a high concentration, it may be due to drug damage.